Emmanuel O.
See all reviews
Master machine learning with Naïve Bayes: learn the theoretical foundations behind the Bayesian approach and gain practical problem-solving skills






Skill level:
Duration:
CPE credits:
Accredited

Bringing real-world expertise from leading global companies
Master's degree, Theoretical and Mathematical Physics
Description
Curriculum
Free lessons

1.1 What does the course cover?
4 min

1.2 Motivation
4 min

1.3 Bayes' thought experiment
3 min
1.5 Assignment 1
1 min
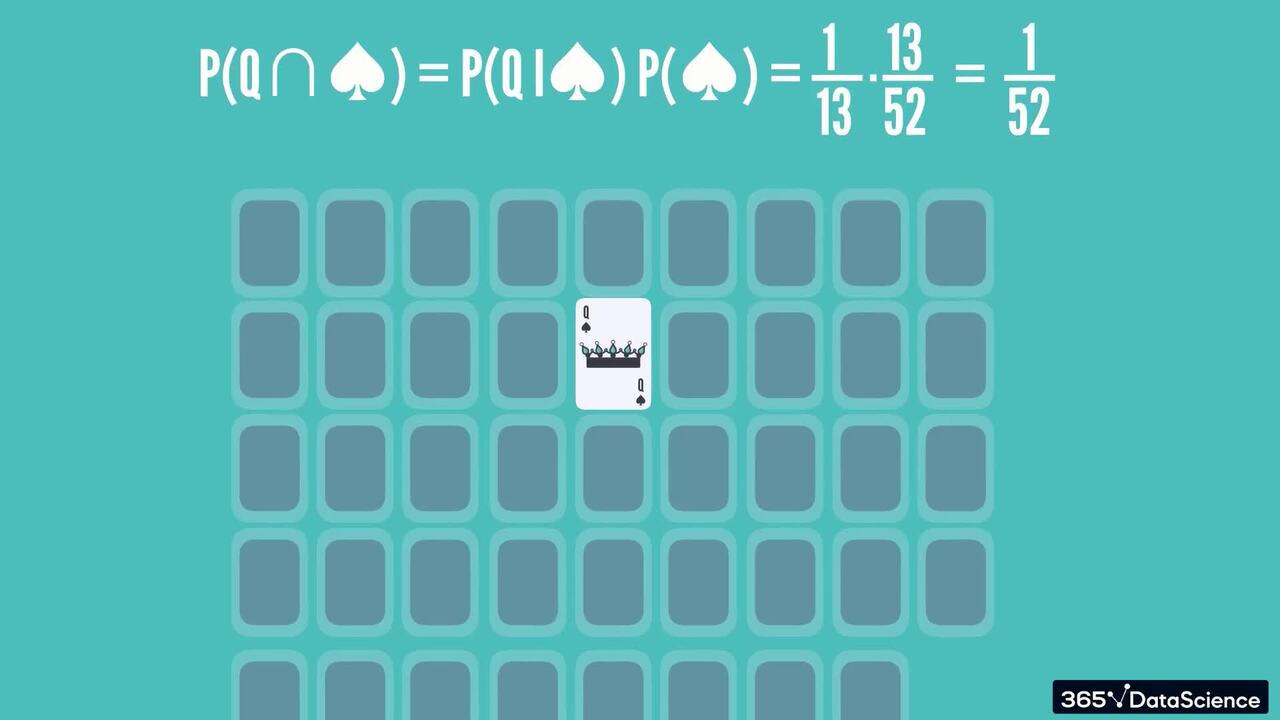
1.6 Bayes' theorem
7 min
1.8 Assignment 2
1 min
94%
of AI and data science graduates
successfully change
#1 most reviewed
9 in 10
people walk away career-ready
ACCREDITED certificates
Craft a resume and LinkedIn profile you’re proud of—featuring certificates recognized by leading global
institutions.
Earn CPE-accredited credentials that showcase your dedication, growth, and essential skills—the qualities
employers value most.





Certificates are included with the Self-study learning plan.

How it WORKS