Python
Explore the Flashcards:
A high-level, interpreted programming language known for its clear syntax and readability,
widely used for data analysis, artificial intelligence, scientific computing, and more.
Package
A collection of pre-written functions, classes, and methods which are capable of handling
and manipulating data and calculating results.
Library
A collection of modules or functions that can be included in applications to provide specific functionality or features, reducing the amount of code developers need to write.
Module
A file containing Python definitions and statements. Modules enable logical organization of Python code and facilitate reusable code libraries.
NumPy
A Python library that provides support for multi-dimensional arrays and matrices,
and a collection of mathematical functions to operate on these arrays.
Works in a lower-level language, which means shorter computation times.
Pandas
A Python library that provides data manipulation and analysis tools,
particularly offering data structures and operations for manipulating numerical tables and time series. Stores multiple types of data simultaneously.
Convention
A set of recommended practices or coding styles that programmers agree to follow to ensure consistency and improve readability in their codebase.
Alias
A shorter or alternative name defined for a module or object in Python, used to shorten code or avoid naming conflicts.
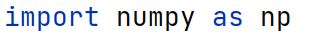
Function
A block of organized, reusable code that performs a specific task; functions provide better modularity for applications and a high degree of code reusing.
Universal Functions
Functions in NumPy that operate element-wise on arrays, providing fast and efficient mathematical functionalities across arrays.
Method
A function that is associated with an object or class in object-oriented programming and is called using that object.
Class
In object-oriented programming, a blueprint for creating objects (a particular data structure), providing initial values for state (member variables)
and implementations of behavior (member functions or methods).
N-D Array Class
N-Dimensional array. In NumPy, this refers to the ndarray class, which represents a multidimensional, homogeneous array of fixed-size items, providing efficient storage and manipulation of numeric data.
Dimensional Array
0-D array - a single data point (scalar)
1-D array - a sequence of values (vector)
2-D array - a collection of 1-D sequences (matrix)
Array
A collection of elements identified by index or key, typically stored so that the position of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula.
NumPy Array (ndarrays)
The fundamental package for scientific computing with Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays.

Lists
A built-in Python data structure used to store collections of items. Lists are mutable, allowing for items to be added, removed, or changed.
Concatenation
The operation of joining two or more arrays or lists into a single one. In NumPy, concatenation can be done along any dimension.

NumPy Documentation
A collection of instructions about all the functions, methods, and classes within a module
and details on how to use them.
dtype
A data type object in NumPy that describes the kind of elements that are contained within an array, including types like integer, float, and complex numbers.
np.int
A NumPy data type that represents integers. It is equivalent to the C long type and varies in size depending on the platform.
np.int32
A NumPy data type that represents a 32-bit integer.
np.float16
A NumPy data type that represents a half-precision float, which is a 16-bit floating-point number.
np.complex64
A NumPy data type that represents a complex number with two 32-bit floating-point numbers, one each for the real and imaginary parts.
np.bool
A NumPy data type that represents boolean values (True or False).
np.str
A NumPy data type that represents strings.
shape Attribute
Returns a tuple representing the array's dimensions, providing the size of the array along each dimension. Rather than a method, it's not callable (doesn't need "()" at the end). The shapes of the arrays need to be compatible.
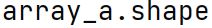
size Attribute
An NumPy arrays attribute that returns the total number of elements in the array, which is the product of the elements of the array's shape.
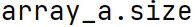
Indexing
The method by which elements of an array or list are accessed using their position number within the array. By adding numbers between square brackets, we can reference specific values of the array. Indexing in Python starts from zero.
Indices (Indexes)
The position numbers used to access specific elements within a data structure like an array or list.
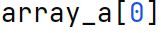
'":" in Indexing
The colon (:) is used in indexing to specify a range of values in arrays. For example, array[start:stop] accesses elements from the 'start' index up to,
but not including, the 'stop' index.
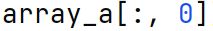
Negative Indices
Negative indices mean traversing from the back. -1 represents the last item, -2 represents the second last, and so forth.
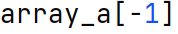
Assigning Values
The process of setting or changing the value of a specific element in an array or list by using its index.
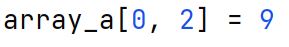
Type Assigment
Refers to specifying the data type of the elements in an array at the time of its creation. Type assignment in Python is dynamic. Hence,
a variable's type can change based on what values we assign to it.
Type Casting
The method of converting an array from one dtype to another in NumPy. This can be done explicitly using the astype() function or implicitly during operations.
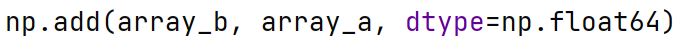
math Library
A Python library that provides access to mathematical functions for floating-point arithmetic, such as trigonometric functions, logarithmic functions, and more.
math.sqrt Function
A function in the math library of Python that calculates the square root of a specified number.
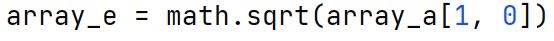
np.sqrt Function
The square root function computes the square root for every element of the array.
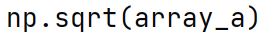
Broadcasting
A feature in NumPy that allows it to perform arithmetic operations on arrays of different shapes by temporarily 'broadcasting' the smaller array across the larger one.

Running over an Axis
Axis = 0 runs the function over every column. Axis = 1 runs the function over every row.
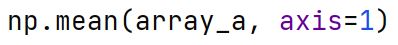
Slicing
A technique used to extract a subset of elements from an array or list using slice notation (start:stop:step).The slices consist of adjacent pieces of data and the slice can contain entire rows and columns of the original array, or just parts of them.
Stepwise Slicing
Specifying a 'step' in slicing allows skipping of elements within the slice range. For example, array[start:stop:step]
accesses elements within the 'start' and 'stop' range at intervals defined by 'step'.
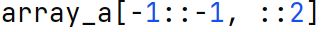
Conditional Slicing
Accessing array elements using boolean expressions that specify which elements to include in the result based on their values.
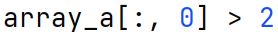
Dimensions
Refers to the number of indices needed to specify an element's position within an array. For example, a 2D array has two dimensions.
squeeze Function
A function in NumPy that removes single-dimensional entries from the shape of an array, simplifying its structure.

np.empty Function
Creates a new array of a specified shape and dtype, without initializing entries, which means it contains random garbage values.
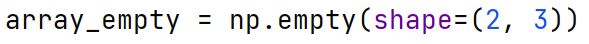
np.ones Function
Creates a new array of a specified shape and dtype, filled with ones.
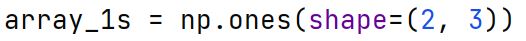
np.zeros Function
Creates a new array of a specified shape and dtype, filled with zeros.

np.full Function
Creates a new array of a specified shape and dtype, filled with a specified fill value.
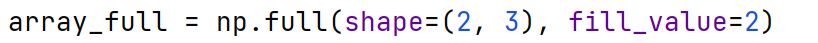
"_like" Functions
Functions in NumPy that create new arrays with the same shape and type as a given array.
np.empty_like Function
Creates a new array with the same shape and type as a given array but without initializing entries, leaving them with random values.
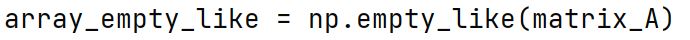
np.arange Functions
Returns evenly spaced values within a given interval.

Random Generators
Functions that generate random numbers from various statistical distributions.
np.random
A module in NumPy that provides a suite of functions for generating random numbers, samples, and distributions.
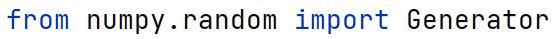
np.normal Method
A method in the np.random module used to draw random samples from a normal distribution.
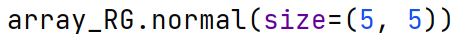
np.integers Method
A method in the np.random module used to generate random integers between given low and high values.
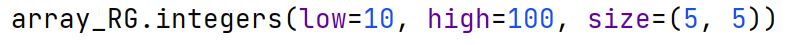
np.choice Method
A method in the np.random module that generates a random sample from a given 1-D array or range.

Distributions
Describe how values are spread or distributed across a dataset. Different types of distributions can model different types of phenomena.
Poisson Distribution
Expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time or space, assuming these events occur
with a known constant mean rate and independently of the time since the last event.
np.poisson Method
A method in the np.random module module that generates random samples from the Poisson distribution.
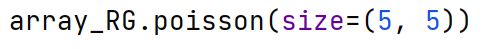
Binomial Distribution
Describes the number of successes in a fixed number of independent Bernoulli trials, each with the same probability of success.
np.binomial Method
A method in the np.random module that generates random samples from a binomial distribution.
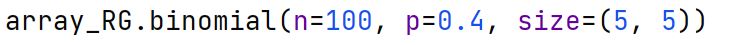
Logistic Distribution
A continuous probability distribution used in logistic regression and can model the chance of a certain event occurring, such as pass/fail, win/lose, alive/dead.
np.logistic Method
A method in the np.random module that generates random samples from the logistic distribution.
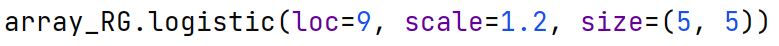
Exponential Distribution
Describes the time between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate.
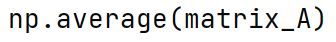
np.exponential Method
A method in the np.random module that generates random samples from an exponential distribution.

Geometric Distribution
A discrete distribution that models the number of trials needed to get the first success in repeated Bernoulli trials.
np.geometric Method
A method in the np.random module that generates random samples from the geometric distribution.

np.transpose Method
A method in NumPy used to permute the dimensions of an array, or to transpose a matrix.
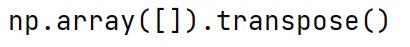
Delimiter
A character or sequence of characters used to specify the boundary between separate, independent regions in plain text or other data streams (e.g., commas in CSV files).

np.load Method
Used to load arrays or pickled objects from .npy, .npz or pickled files.

np.savetxt Method
A method in NumPy used to save an array to a text file, with options to specify the delimiter and other formatting details.

np.genfromtxt Method
A function in NumPy used to load data from a text file, with the ability to handle missing values and flexible type conversion.

np.loadtxt Method
A function in NumPy used to load data from a text file, where each row in the text file must have the same number of values.

CSV
"Comma-Separated Values," a file format used to store tabular data in plain text, where each line corresponds to a data record and each record consists
of fields separated by commas.
np.array_equal Method
Checks if two arrays have the same shape and elements, returning True if they are equal.

np.savez Method
Used to save several arrays into a single file in uncompressed .npz format.
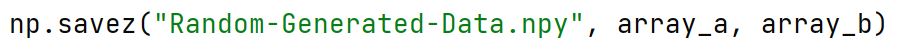
np.min Method
Used to return the minimum value from an array.

np.amin Method
An alias for the min method in NumPy, it performs the same operation and returns the minimum value in an array.
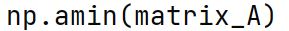
Used to compare two arrays and returns a new array containing the element-wise minima.
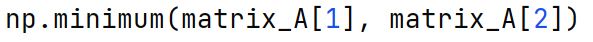
np.minimum.reduce Method
Applies the minimum operation along one axis of an array, reducing its dimension.
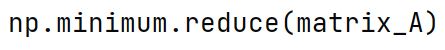
np.max Method
Used to return the maximum value from an array.

np.amax Method
An alias for the max method in NumPy, it performs the same operation and returns the maximum value in an array.
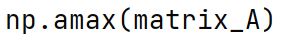
np.maximum.reduce Method
Applies the maximum operation along one axis of an array, reducing its dimension.
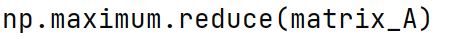
np.ptp Method
Returns the range (maximum - minimum) of values along an axis.

np.sort Method
Sorts an array, either along a specific axis or the entire array if no axis is specified.
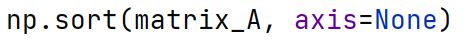
Percentile
A value that is greater than the corresponding % of the dataset.
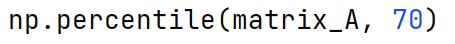
np.percentile Method
Used to compute the nth percentile of the given data (array elements) along the specified axis.
Quantile
A value that is greater than the corresponding part of the dataset.
np.quantile Method
Used to calculate the quantiles of the given data (array elements) along the specified axis.
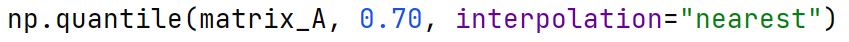
np.median Method
Returns the median (middle value) of the data in the array along the specified axis.
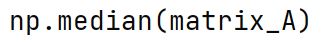
np.average Method
Used to compute the weighted average of elements in an array along the specified axis.
np.mean Method
Calculates the arithmetic mean of elements across the specified axis of an array.
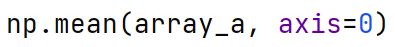
Varience
A statistical measure that represents the degree of spread in a dataset. The more spread out the data, the higher the variance.
np.var Method
Calculates the variance of the array elements along the specified axis.

Standart deviation
A statistic that measures the dispersion of a dataset relative to its mean and is calculated as the square root of the variance.
np.std Method
Computes the standard deviation of array elements along the specified axis.
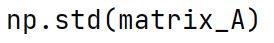
Covarience
A measure used in statistics to determine the degree to which two variables change in tandem (i.e., co-vary).
np.cov Method
Computes the covariance matrix of two or more sets of variables.
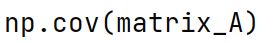
Correlation
A statistical measure that indicates the extent to which two or more variables fluctuate in relation to each other.
np.corrcoef Method
Returns the correlation coefficients of a matrix representing the correlation between every pair of arrays.
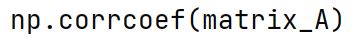
Histogram
A graphical representation of the distribution of numerical data, where the data is divided into bins, and the frequency of data in each bin is represented.
np.histogram Method
Used to compute the histogram of a set of data along with the bin edges.
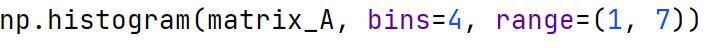
Preprocessing
Refers to the operations applied to raw data to make it suitable for further analysis, often involving normalization, scaling, handling missing data,
and encoding categorical variables.
NaN Values
Not A Number. Refers to missing or unpresentable values within a NumPy array.
np.isnan Method
Used to check element-wise for NaN in the array and returns a Boolean array indicating the presence of NaNs.
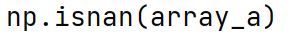
np.delete Method
Returns a new array with sub-arrays along an axis deleted from the original array.
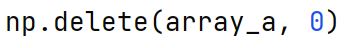
Argument Functions
Functions that return indices, positions, or arguments where certain conditions are met, useful for data sorting and filtering.
np.argsort Method
Returns the indices that would sort an array along a specified axis.
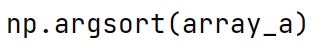
np.argwhere Method
Finds the indices of array elements that are not zero, grouped by element.

Shuffling Data
A process where the order of data in an array is randomized, often used to ensure that models do not learn anything from the order of data.
Seeds don't work for shufling.
np.random.shuffle Method
Used to modify a sequence in-place by shuffling its contents.
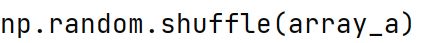
Casting
Refers to changing an object from one data type to another, such as from an integer to a float in NumPy.
Stripping Data
The process of cleaning data by removing unwanted parts, such as leading/trailing spaces or invalid characters.
Stacking
A technique in NumPy that involves joining a sequence of arrays along a new axis.
np.unique Method
Finds the unique elements of an array and returns these unique elements, optionally returning associated indices or counts.

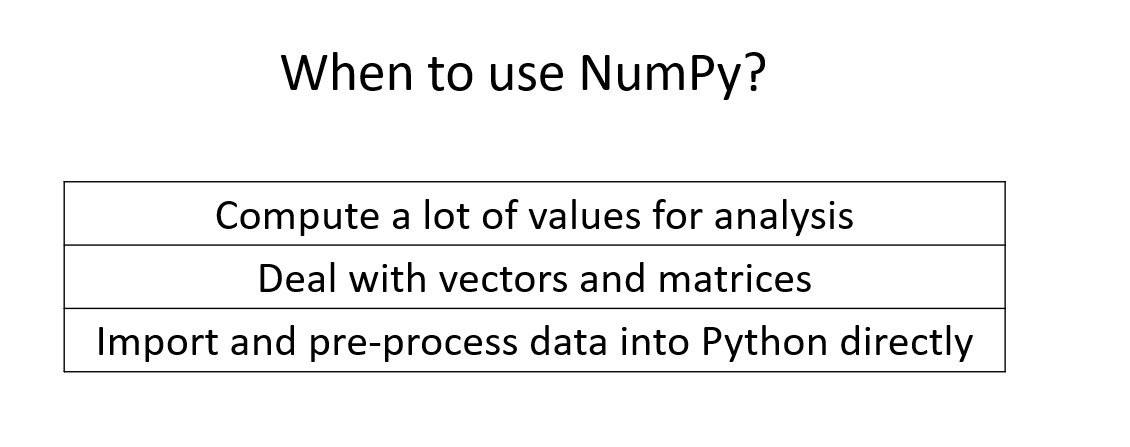
When to use NumPy?
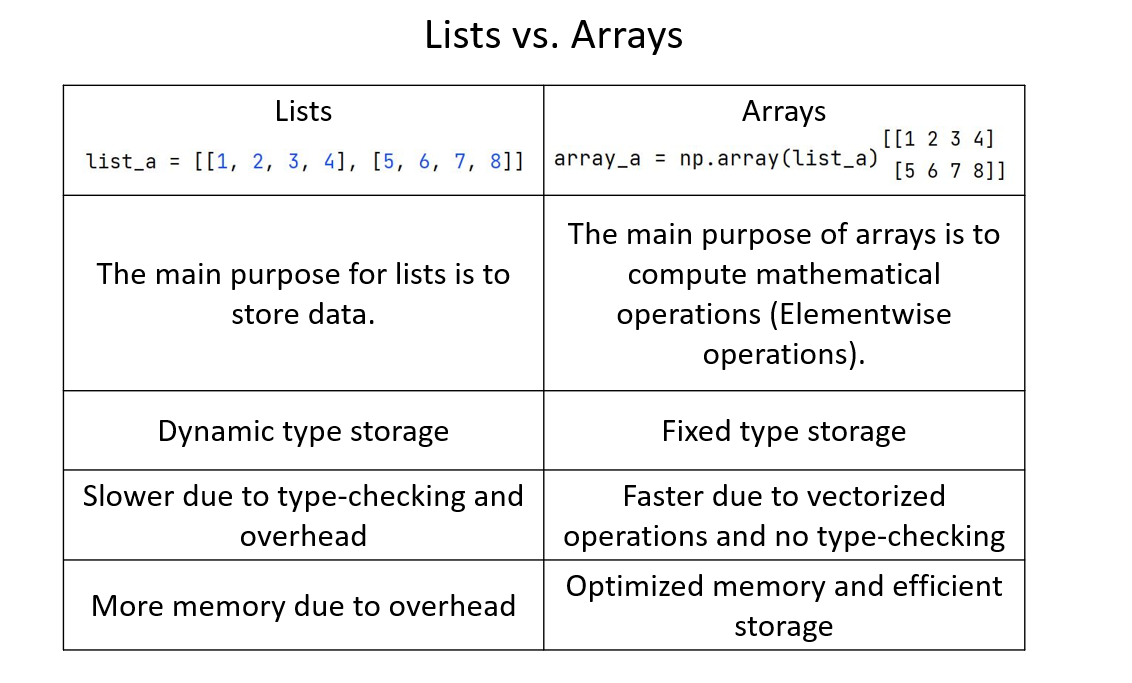
Lists vs. Arrays
Given the following array, what will the result of the print function be?
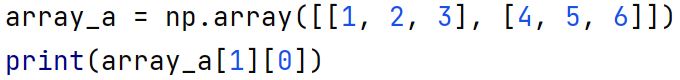
4
Given the following array, what will the result of the print function be?
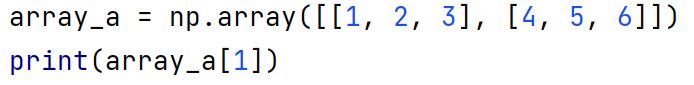
[ 4 5 6 ]
Given the following array, what will the result of the print function be?

[ 1, 2, 3, 2 ]
Given the following array, what will the result of the print function be?

[ [ 2 4 6 ]
[ 8 10 12 ]]
Broadcasting Rules

Given the following array, what will the result of the print function be?

[ [ 1 ]
[ 2 ] ]
Given the following array, what will the result of the print function be?

[ [ 1 ]
[ 2 ] ]
Given the following array, what will the result of the print function be?

[ [ 1 ] ]
Given the following array, what will the result of the print function be?

[ ]
Given the following array, what will the result of the print function be?

[ [ 4 3 0 ]
[ 3 6 4 ]
[ 1 1 0 ] ]
Given the following array, what will the result of the print function be?

[ False True False ]
Conditions
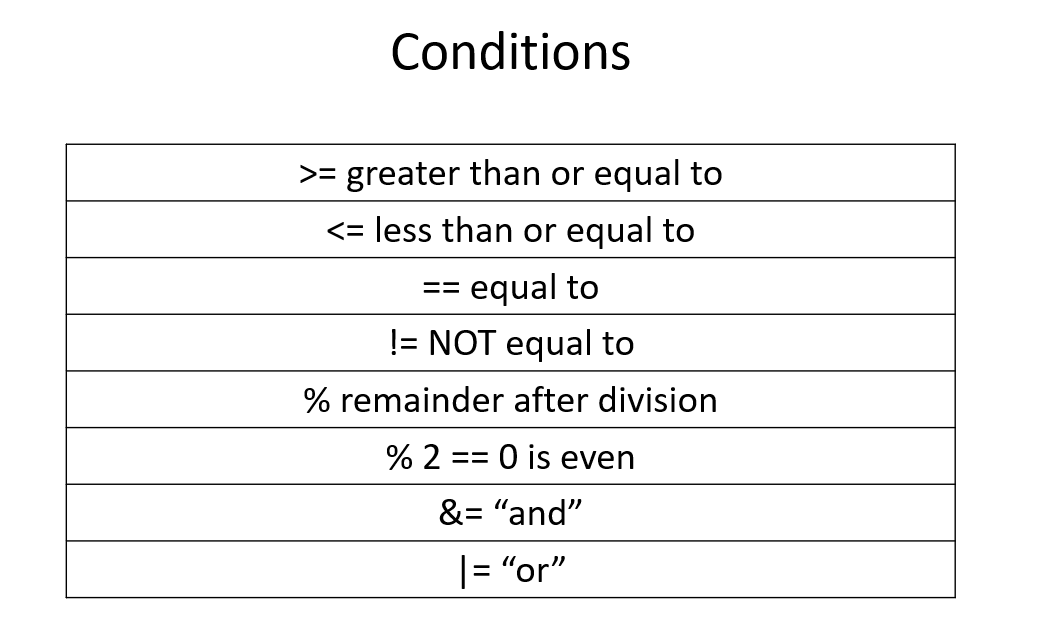
Given the following array, what will the result of the function be?

2.0
Given the following array, what will the result of the function be?

[ 2.5 3.5 4.5 ]