Data Strategy
Explore the Flashcards:
A strategy that helps you identify a manageable number of
strategic data use cases.
A Good Data Strategy
It is not determined by what data the company has readily
but what the business wants to achieve and how data can help to get there.
Data Use Cases
Scenarios or problems where data can be utilized to drive business value or solve specific challenges.

Use Case Owner
A person responsible for a specific use case.
Proactive vs. Reactive Strategies
Anticipating versus responding to trends and issues.
Business Intelligence
Using technology to analyze data for improved business decisions.
Business Analytics
The use of data and statistical methods to improve business performance.
Digital Transformation
Integrating digital technology into all business areas for fundamental operational changes.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The process of making organizational decisions based on actual data rather than intuition or observation alone.
Self-Service
A company gives more people access to the right data and tools
so they can use it to answer their business questions.
Curated Dashboards
A company does not provide access to raw data but instead works on determining the
right data to be used and design sophisticated dashboards intended for decision-makers.
Business Dashboard
'A simple visual display of the most important information that decision-makers need to help them achieve objectives.
KPIs
Key Performance Indicators are quantifiable measures used to evaluate the success of an organization or of a particular activity in which it engages.
KPI Dashboard
A way to communicate insights from key performance indicators to the people who need them.
Gives decision-makers quick access to the critical indicators or instruments of the business.

Operational Dashboard
Allows monitoring of day-to-day processes and outputs of your business. Provides information that allows you to fix issues before they become problems.
Strategic Dashboard
Looks to the future and seeks to identify obstacles and challenges that you may face on the way to achieving your strategic goals.
KBQs (Key business questions)
The biggest unanswered questions about an organisation.
They focus our attention on what really matters by putting data into context
and provide guidance for collecting meaningful and relevant data.
They should be short and clear and be focused on the present and the future.
Closed Questions
Easy to answer questions with a short and specific response. Usually seek simple facts.
Open Questions
Invite the respondent to thoughts, explanations, and expressed opinions. Usually seek an open-ended response.
Is this an open or a closed question?
What is the market share of product X?
Closed question.
Is this an open or a closed question?
To what extent are we improving our market share of product X?
Open question.
What should KBQs focus on?
The present and the future.
KBQs should be…
Short and clear.
Buzzwords
Popular or fashionable jargon used in the business and technology sectors to capture the essence of trends, innovations, or concepts.
KBQs should not include buzzwords.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
A compiled list of common questions and answers on a particular topic, designed to address the most typical concerns,
issues, or topics of interest for users, customers, or stakeholders.
Annotations
Notes or comments added to data to provide context or explain certain data points.
Data Customers
A person who will be using the data and learning from the insights generated.
Data Skills
The ability to process, analyze, and extract meaningful information from data.
Data Literacy
Training and emphasis on developing data-related skills.
Data Exploration Tools
Technologies enabling users to examine and analyze data for patterns and insights.
Data Translator
A person who connects the analytics and the business team.
Data Storytelling
The practice of building a narrative around data and its analysis to communicate insights in a compelling and understandable way.
Data Relevance
Ensuring data collected is directly related to the business questions being addressed.
Data Contextualization
Putting data into a relevant context to enhance communication and decision-making.
Data Packaging
The practice of presenting data in a well-structured and digestible format.
Data Reduction
Simplifying datasets by reducing variables.
Data Consolidation
Merging data from multiple sources to improve analysis and decisions.
Data Objective
A specific, measurable goal that an organization aims to achieve using data.
Data Collection
The process of gathering information from various sources for use in analysis and decision-making.
Data Explosion
The rapid increase in the volume of data generated and stored in recent years.
Data Processing
The series of operations on data to convert it into useful information.
Data-Enabled Automation
Using data to automate business processes via AI and machine learning.
Data Management
The practice of collecting, keeping, and using data securely, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
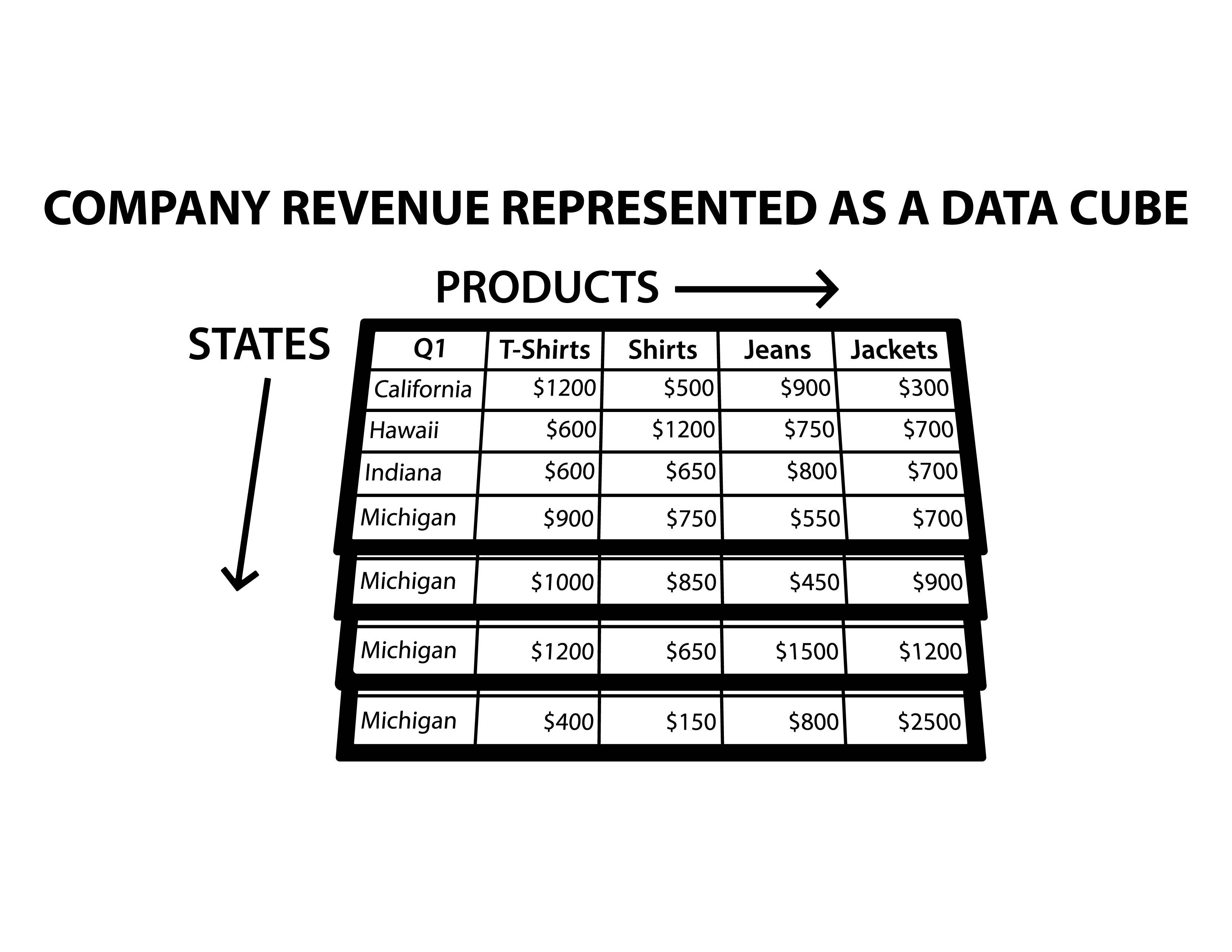
Data Cubes
A multi-dimensional array of values, typically used to describe data in terms of dimensions and facts.
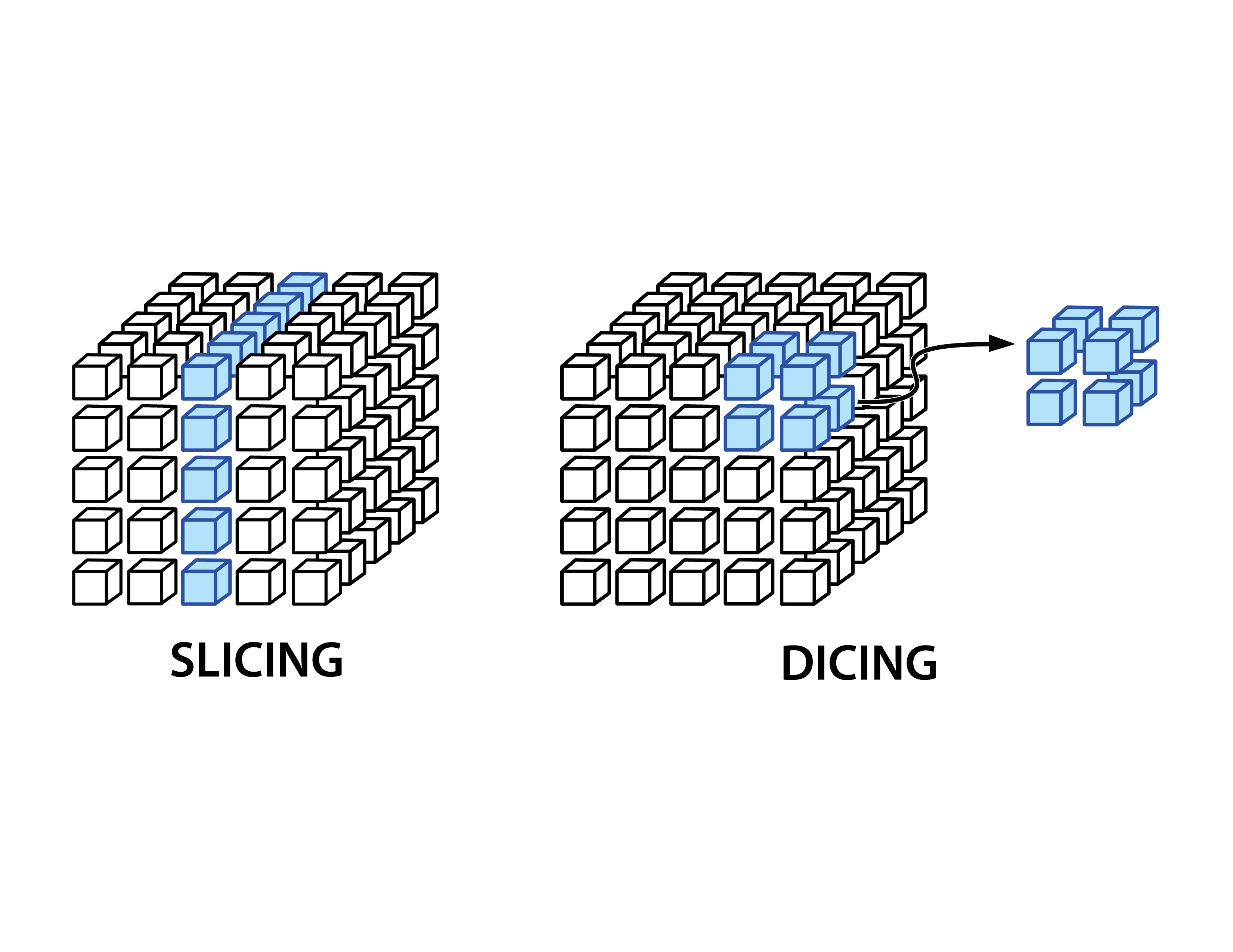
Slice and Dice
The ability to break down data into smaller segments, allowing for detailed analysis and examination of different facets of the data.
Data Sets
A collection of data points or records, typically organized in a structured format.
Data Metrics
Quantifiable measures used to track and assess the status of specific business processes.
Data Sourcing
The process of identifying, evaluating, and accessing the necessary data from internal
and external sources required for business operations, analysis, and decision-making.
Data Governance
A collection of practices and processes which help to ensure
the formal management of data assets within an organization, including data integrity, data quality, and data security.
Data Quality
The condition or quality of data, which includes factors such as accuracy, completeness, reliability, and relevance.
Data Monetization
The process of using data to generate monetary value.
Data Democratization
The practice of making data accessible to all members of an organization, not just specialized data professionals.
Data Ethics
The branch of ethics that focuses on the responsible and ethical management of data, especially personal data.
Data Privacy
The aspect of information technology that deals with the ability an organization or individual
has to determine what data in a computer system can be shared with third parties.
Data Ownership
The legal rights and complete control over a single piece or set of data elements.
Access Rights
The permissions granted to users or systems to access, use, or control data.
Data Security
Protective measures that ensure data is kept safe from corruption and that access to it is suitably controlled.
Data Concealment
Identifying hidden or forgotten data within the company.
Data Commodity
The concept of using data as a tradeable asset or business commodity.
Data Providers
Companies or organizations that specialize in collecting and selling data, like Experian, Amazon, IBM.
Data Repositories
Centralized places where data is stored and managed. Data repositories can be structured to support various types of data,
including but not limited to structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Deep Face
Refers to deep learning techniques used in facial recognition systems.
Deep Text
Refers to deep learning techniques used in processing and understanding human language in textual form.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
Defines standardized data protection laws.
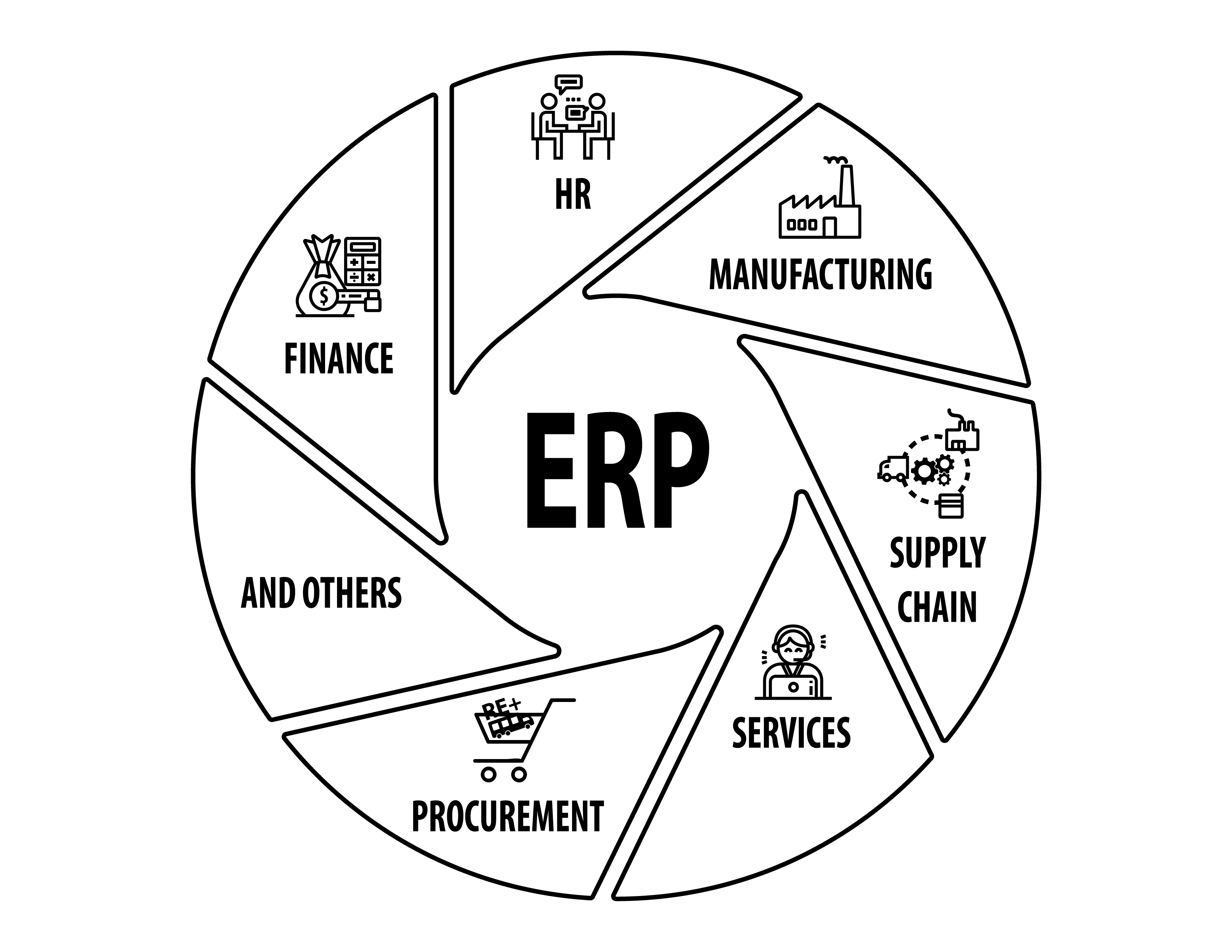
ERP System
Systems integrating various business processes into a unified framework.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Total value a customer contributes over their relationship duration.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
A metric measuring customer loyalty based on their likelihood to recommend.
Churn Rate
The rate at which customers cease business with a company, indicating retention and loyalty.
Holistic Customer View
Integrating data from various services for a comprehensive understanding of customers.
Pulse Surveys
Frequent, brief surveys to gauge customer sentiments and satisfaction regularly.
Types Of Data
The various classifications of data such as quantitative, qualitative, categorical, and numerical.
Categorical Data
Data that can be divided into groups or categories that do not have a natural order.
Numerical Data
Data that is expressed in numbers and can be ordered or ranked.
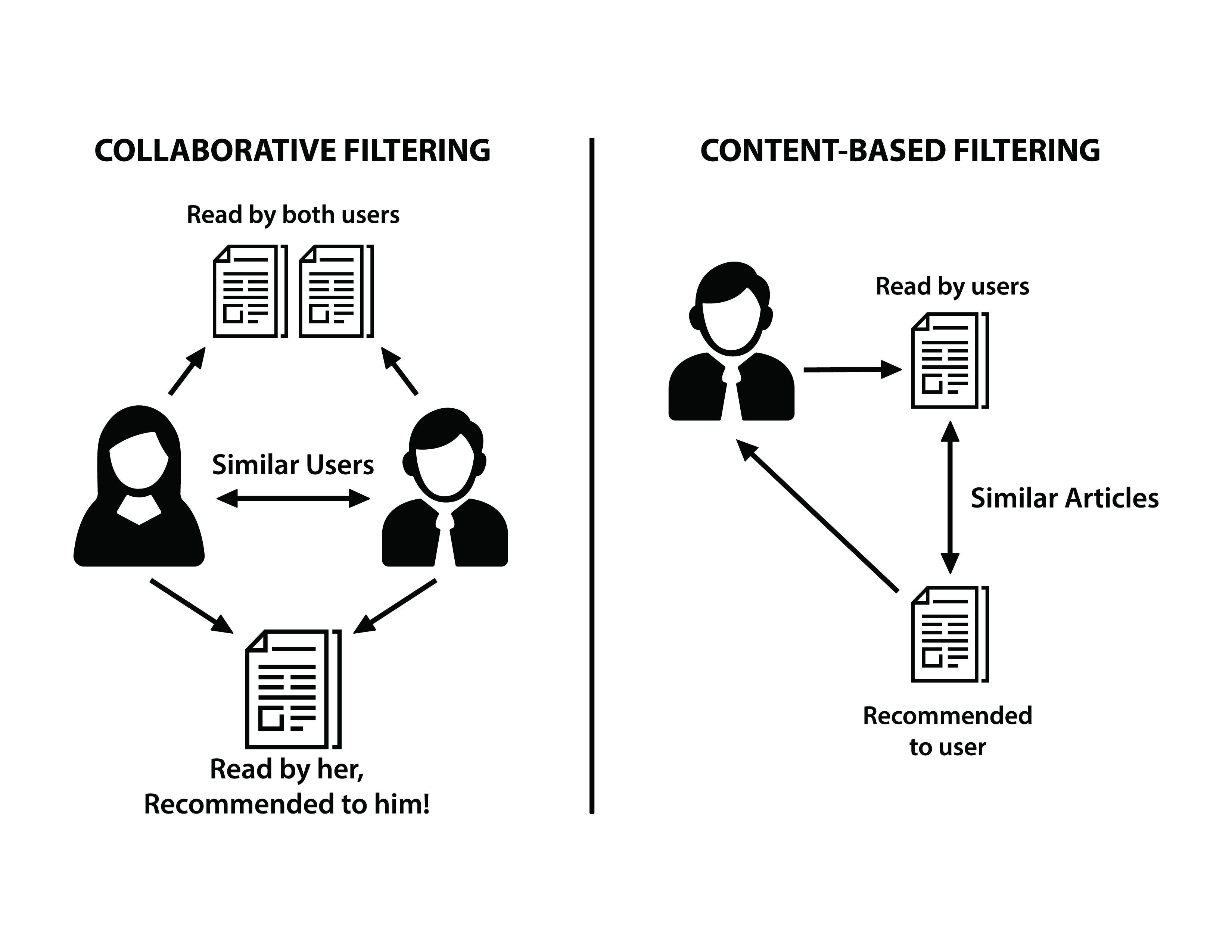
Collaborative Filtering
A method used by recommender systems to make predictions about the interests of a user by collecting preferences from many users.
Artificial Intelligence
The simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems.
Machine Learning
A branch of artificial intelligence that involves the creation of algorithms
that can modify themselves without human intervention to produce desired outputs.
Algorithms
A process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations, especially by a computer.
Recommendation Systems
Algorithms predicting and displaying items a user is likely to be interested in.
Decision Support Systems
Computer-based systems assisting in organizational decision-making through data and analytical tools.
Cobots
Collaborative robots designed to work alongside human workers, enhancing the capabilities of the human workforce.
Machine Vision
The technology and methods used to provide imaging-based automatic inspection and analysis for applications
such as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance.
Cloud Technologies
Technologies that allow users to access data, applications, and services over the Internet,
eliminating the need for physical hardware and enabling scalable resources.
Micro-Moment
An intent-rich moment when a person turns to a device to act on a need to learn, do, discover, watch, or buy something.
Data Format
The structure in which data is stored, processed, and used.
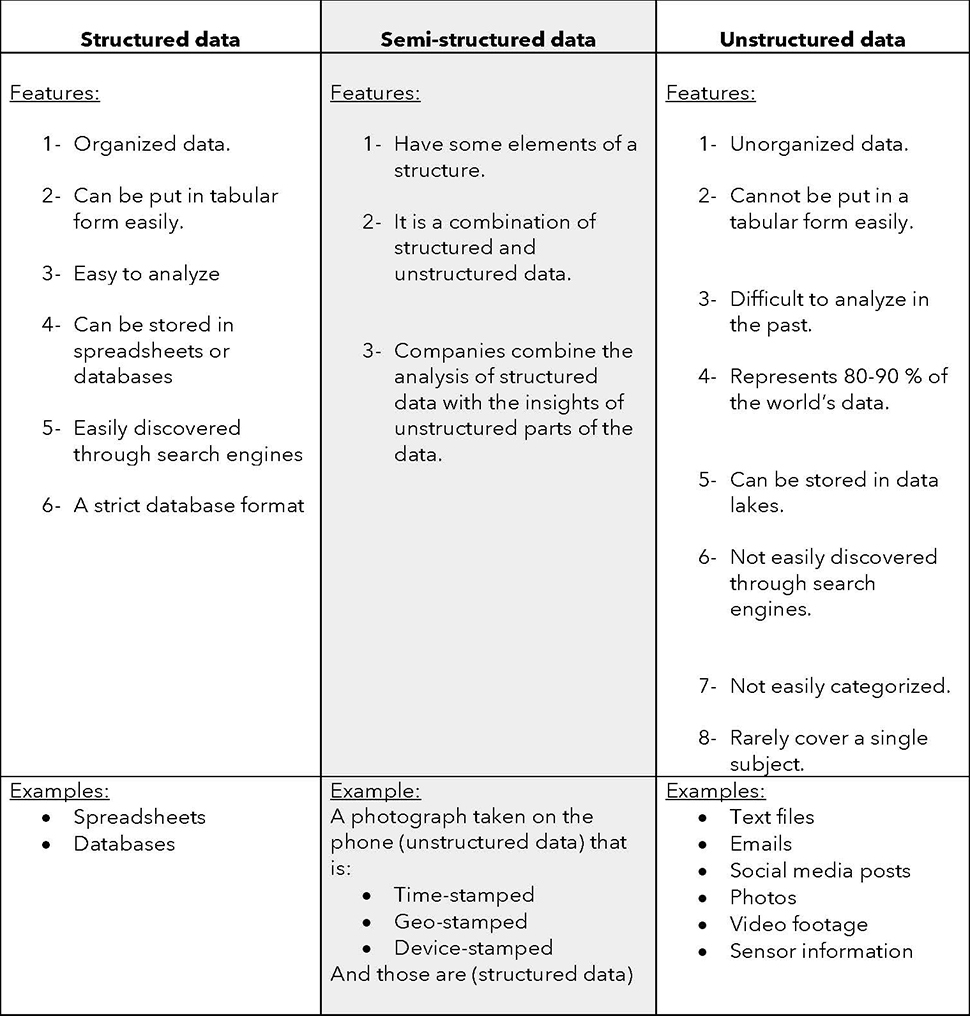
Structured Data
Data that adheres to a pre-defined data model and is easy to analyze.
Semi-Structured Data
Data that does not conform to a data model but has some organizational properties that make it easier to analyze.
Unstructured Data
Information that does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner.
Structured vs Unstructured vs Semi-Structured data
Internal Data
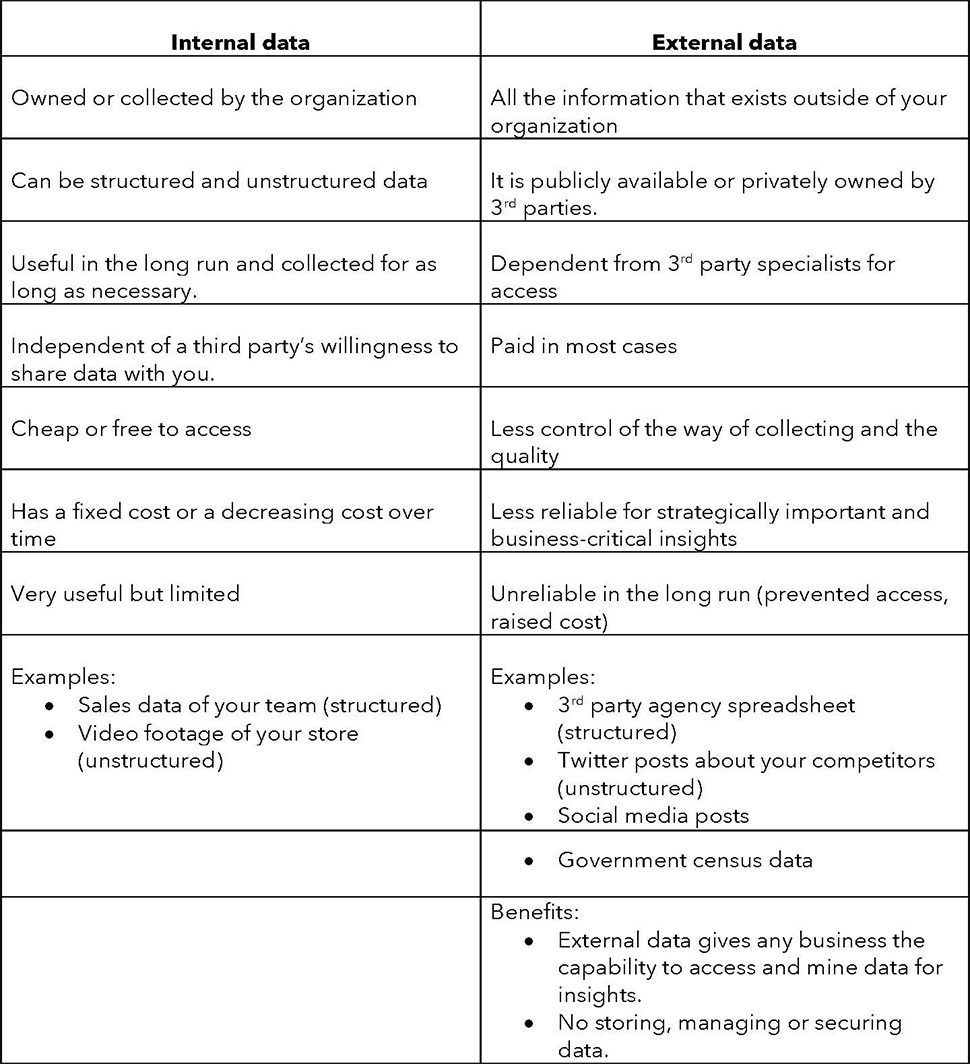
Data that originates from within the organization.
External Data
Data that is sourced from outside the organization.
Internal vs External data
Metadata
An underlying definition or description of data. Data that describes other data.