SQL (Structured Query Language)
Explore the Flashcards:
A programming language used for managing and manipulating relational databases.
Database Managers
Professionals responsible for managing and overseeing database management systems (DBMS).
Data Manipulation
The process of modifying data to make it more organized and readable.
Database
An organized collection of structured information, stored electronically.
Database Designer
A professional responsible for designing the structure, architecture,
and layout of a database, ensuring it meets user requirements and business needs.
Data Integrity
The accuracy, consistency and reliability of the data stored in a database.
Data Extraction
The process of retrieving data from various sources for further data processing or analysis.
Data Consistency
Ensuring that data across a database remains accurate and uniform throughout various operations and transactions.
Data Security
Measures and practices implemented to protect data from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft throughout its lifecycle.
Database Administration
The process of managing, maintaining, and overseeing a database system.
Database Administrator
A professional responsible for managing, maintaining, and overseeing a database,
ensuring its optimal performance, security, and reliability.
Database Management System (DBMS)
Software enables users to store, modify, extract, and query data in a database.
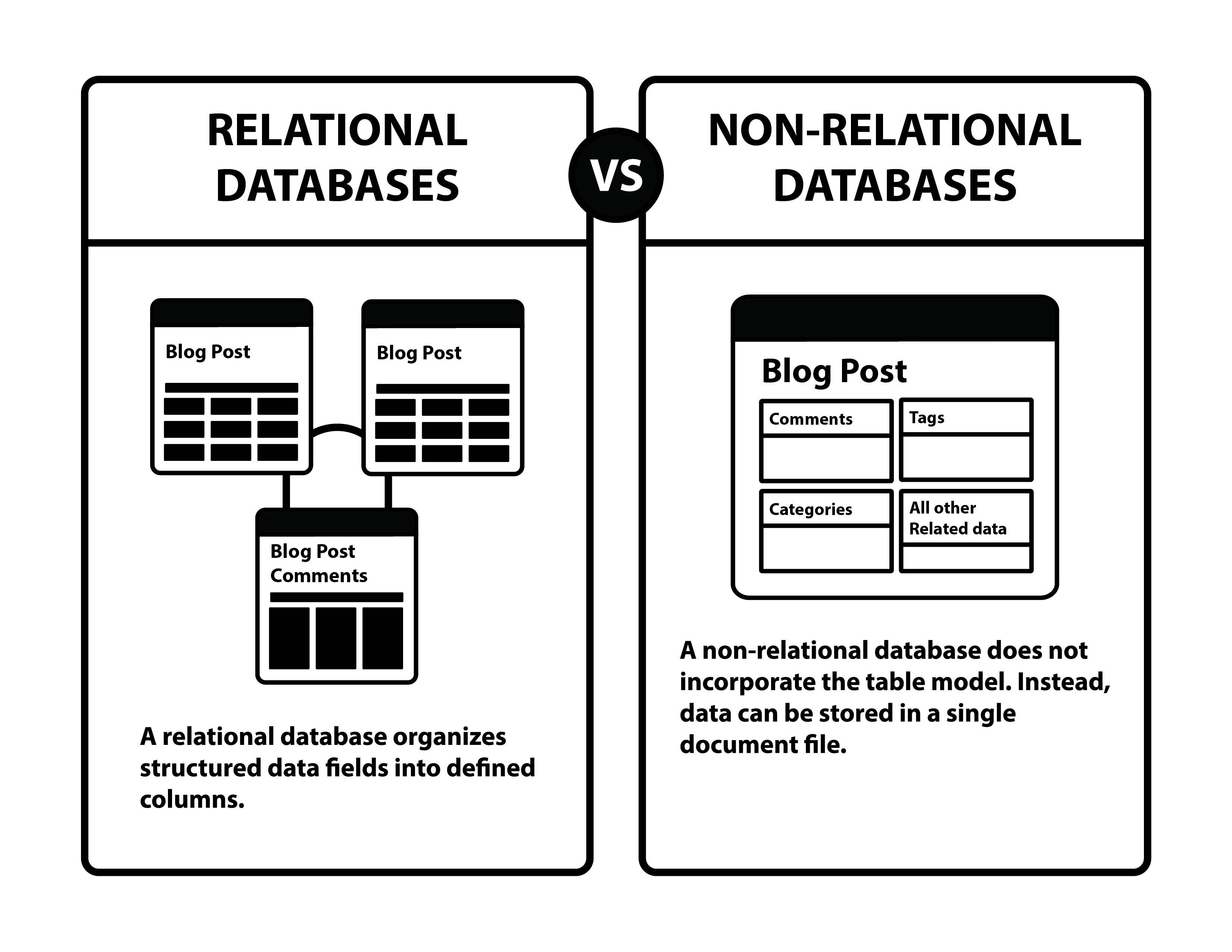
Relational Database
A type of database that organizes data into tables related to each other through common data columns, providing a way to establish relationships between different data points.
Non-relational Database
A type of database that stores and retrieves data without requiring data to be stored in tables.
Relational Algebra
A set of operations used to manipulate and retrieve data from relational databases based on set theory.
Efficiency in Data Retrieval
The effectiveness and speed at which data can be accessed from a database.
Data Storage and Memory Space
The way data is saved in a database and the amount of disk space it occupies.
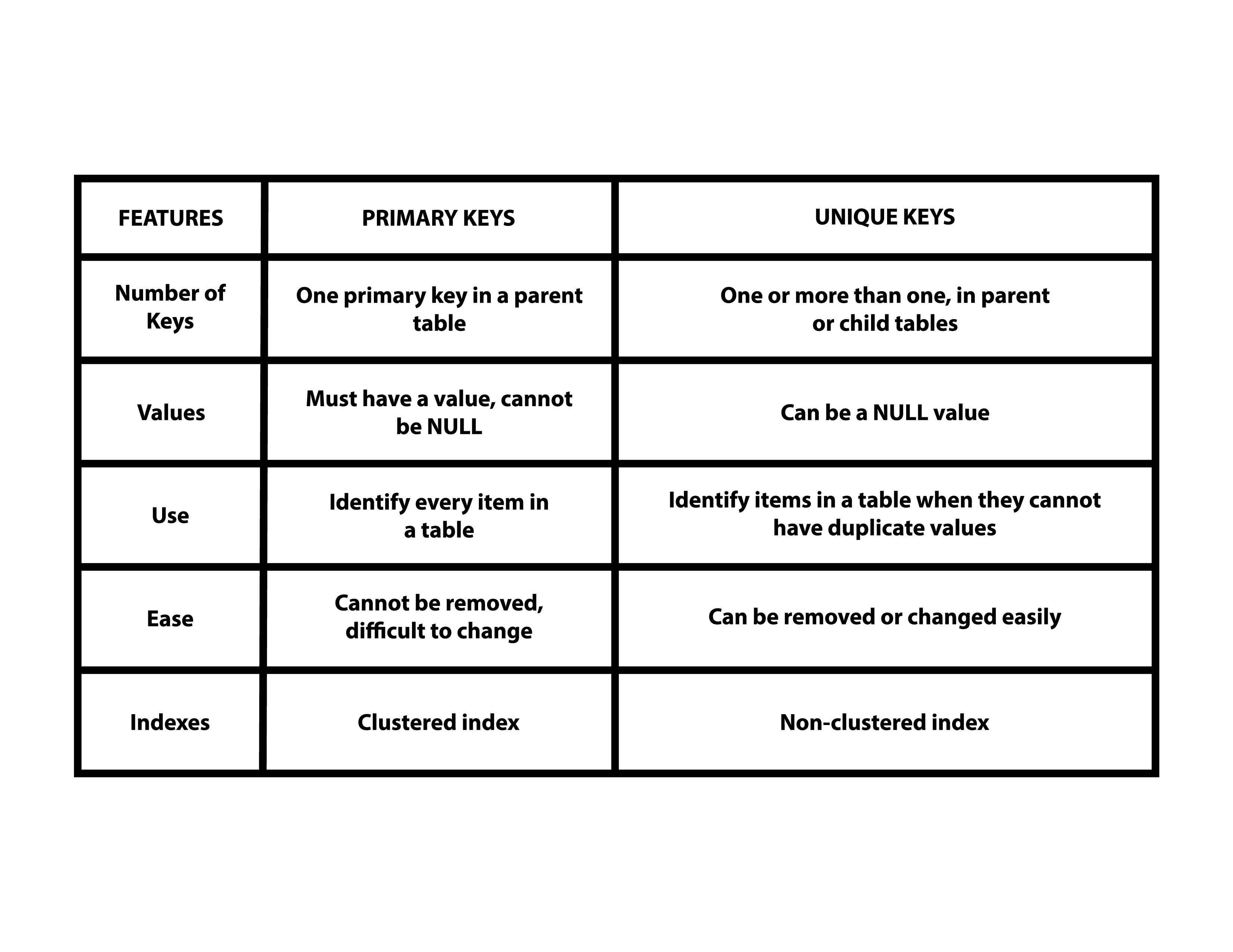
Common Fields in Database Tables
Fields that appear in multiple database tables, often used to create relationships between tables.
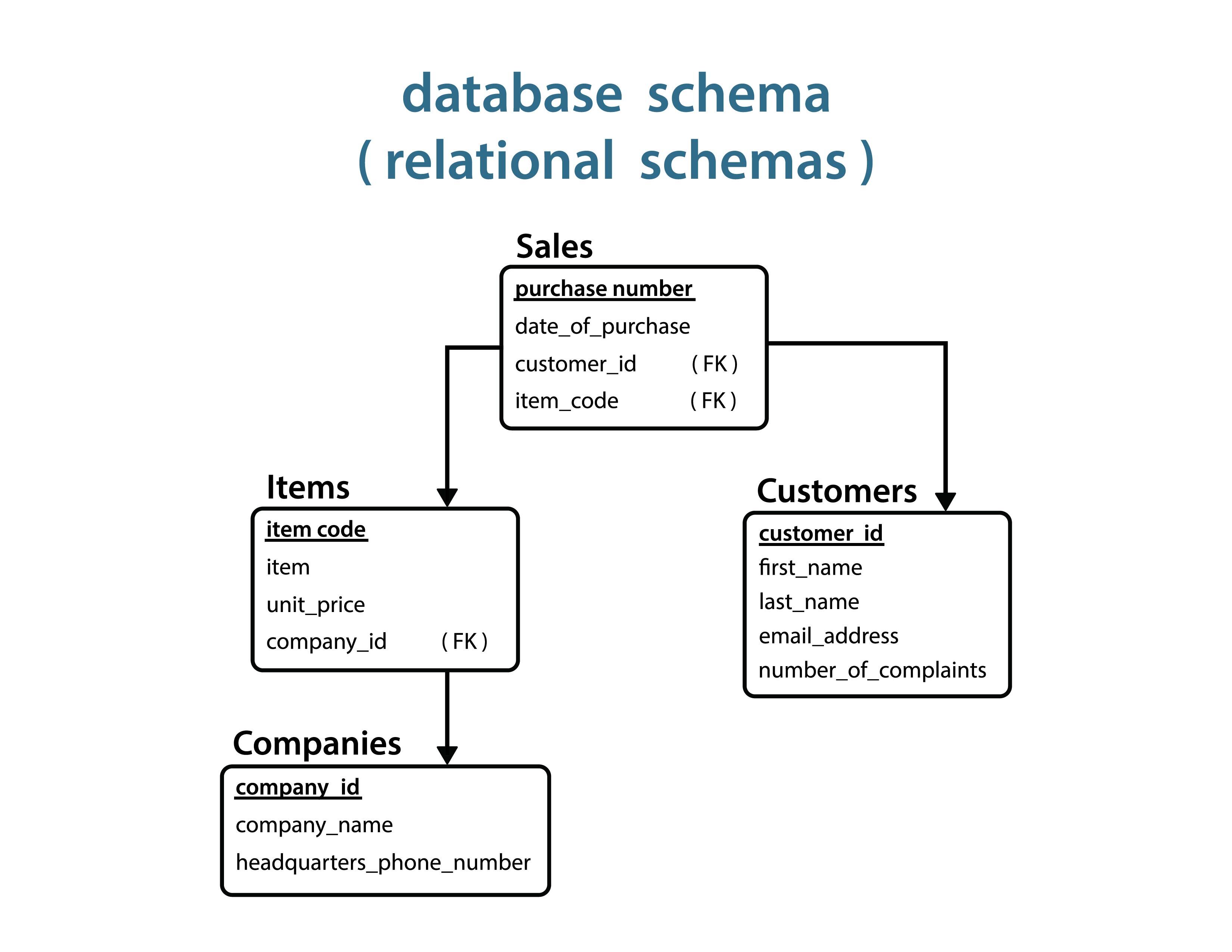
Database Schema
The structure of a relational or non-relational database defined in terms of database tables, views, and constraints.
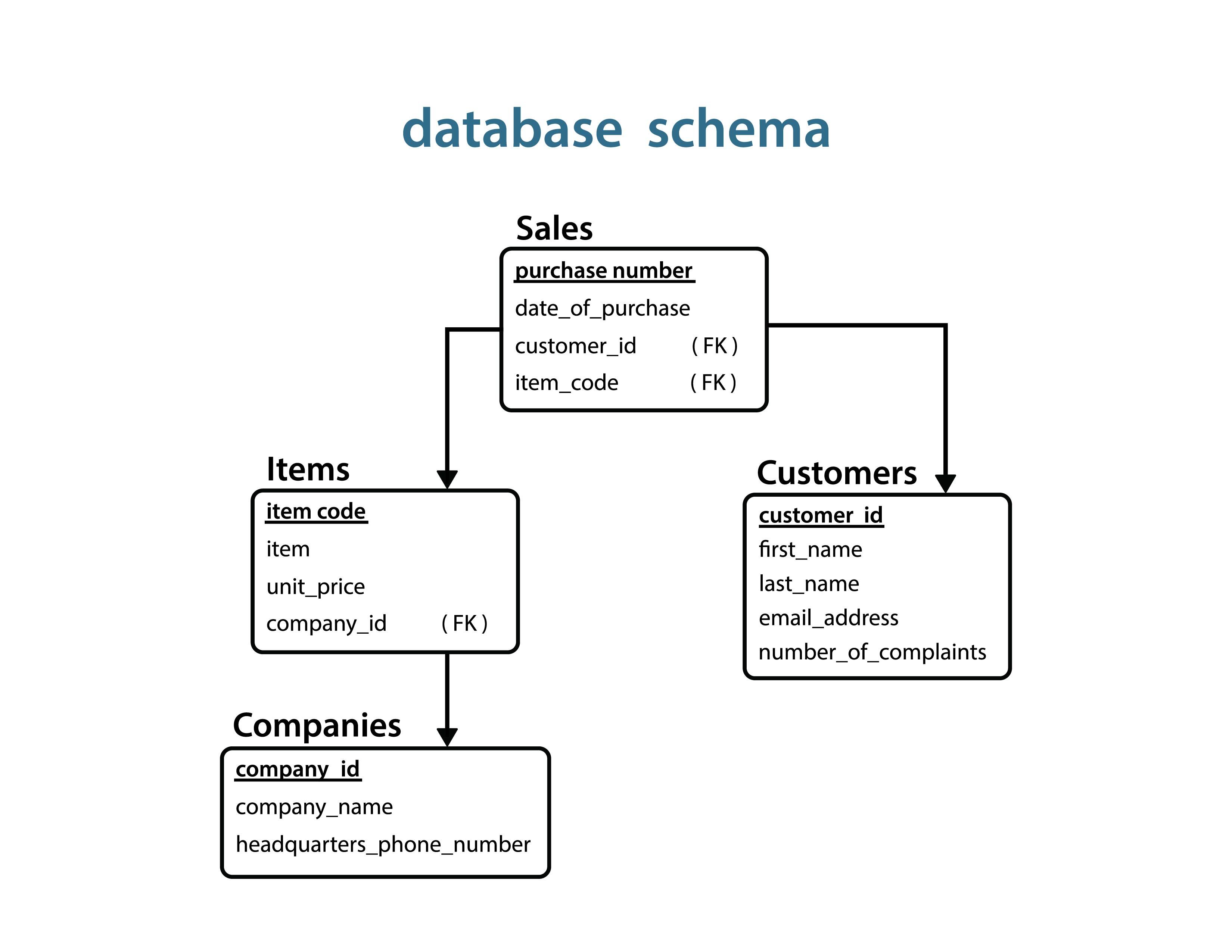
Relational Schema
A blueprint of a relational database that outlines how data is organized into tables.
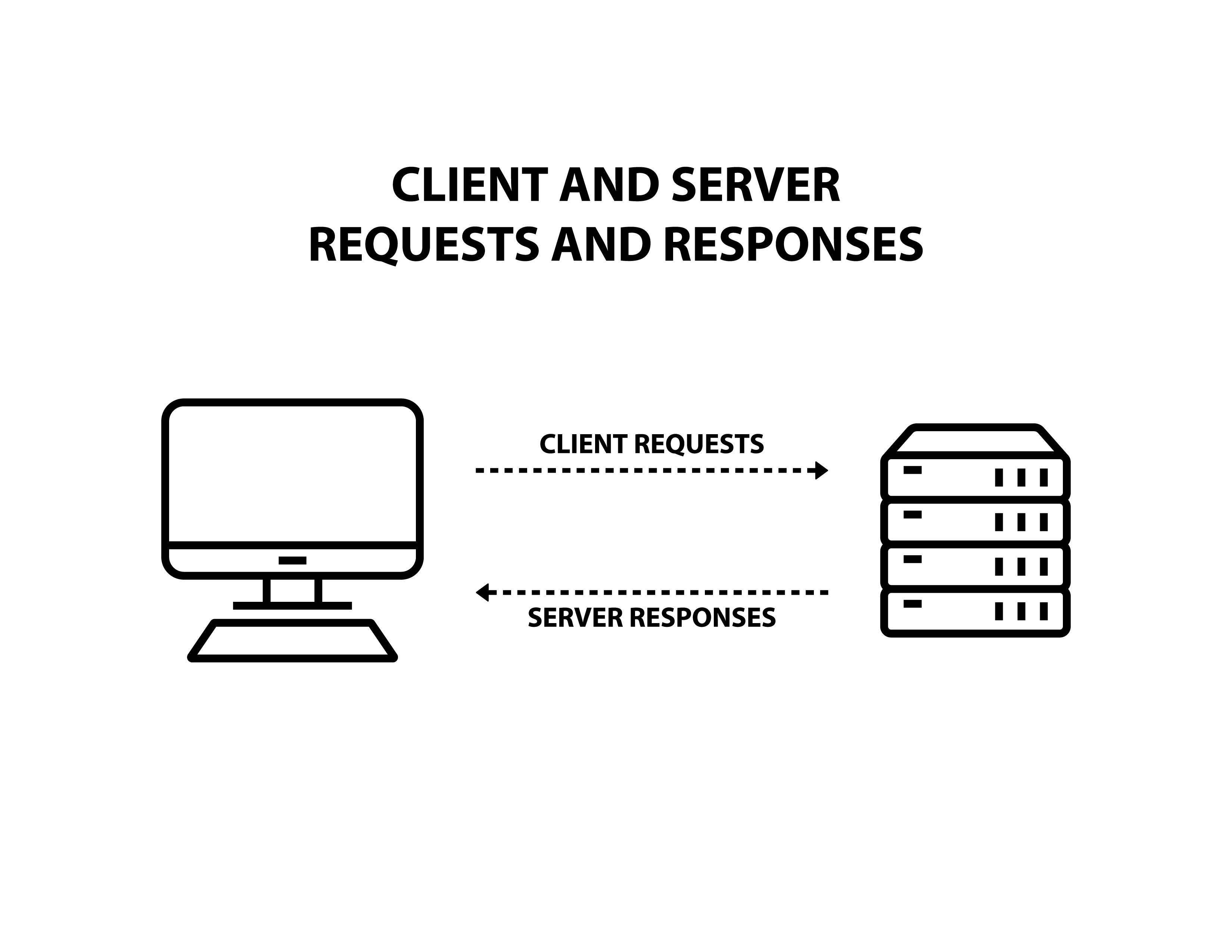
Client-Server Model
An application structure distributing the tasks of an operation between a server (where the server hosts, delivers and manages most
of the resources and services to be consumed by the client) and a client (where the client requests the services).
Entity-Relationship Model
A diagrammatic representation of entities and their relationships, applicable mainly to relational databases.
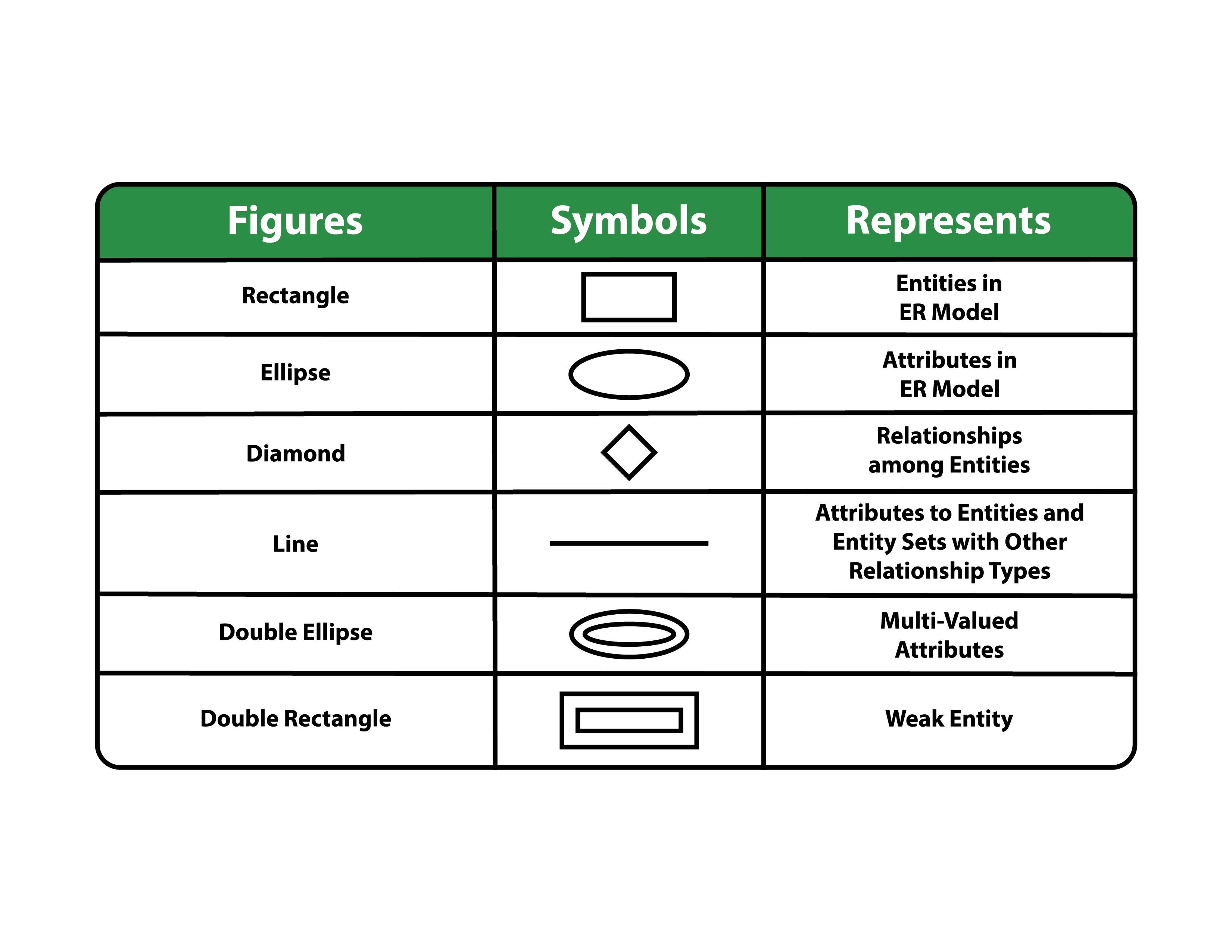
Entity-Relationship Diagram (ER Diagram)
A visual representation of the relationships between different entities in a database.
Database Server
A server that provides database services to other computer programs or computers.
Client Application
Software that accesses a service made available by a server.
Open-source
Software for which the original source code is made freely available to users and may be redistributed and modified.
Open-source Software
Software for which the original source code is made freely available to users and may be redistributed and modified.
MySQL
An open-source relational database management system.
MySQL Workbench
A visual database interface for MySQL that integrates data modelling, SQL development, and
comprehensive administration tools.
MySQL Server
A relational database management system that uses MySQL for data management, storage, and retrieval.
MySQL User
An account in MySQL that has specific privileges, allowing the user to perform actions like query execution,
database management, or more.
MySQL Connection
A link established between a MySQL client and a MySQL server to facilitate communication and data exchange.
Result Grid/Result Set
The visual representation in MySQL of the data returned by a SELECT query, displayed in a tabular format.
Oracle
A multinational computer technology corporation that sells database software and technology, cloud engineered systems
and enterprise software products.
SQLite
A C-library that implements a small, fast, self-contained SQL database engine.
PostgreSQL
An open-source relational database system
with an emphasis on extensibility and standards compliance.
MariaDB
A commercially supported version of MySQL intended to remain free under the GNU GPL.
Microsoft Access
A Microsoft relational database management system intended for working with relatively smaller datasets.
Record
A single, implicitly structured data item in a table.
Entity
An object, concept, person, or thing with an independent existence in the user's domain of interest.
Entity Instance
A single occurrence of an entity.
Localhost
A hostname that refers to the current device used to access the database.
Table Fields in Relational Schema
Columns in a table of a relational database, representing individual attributes of the records in the table.
SQL's syntax
Comprises SQL rules, statements and expressions that allow you to perform various commands and operations.
Data Definition Language (DDL)
A set of statements that allow the user to define or modify data structures and objects, such as tables.
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Allows manipulation of data in tables of a database.
Data Control Language (DCL)
Manages user rights in a database.
Transaction
A sequence of one or more SQL operations executed as a single logical unit of work.
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
Manages the way changes are saved in a database.
Not necessarily every change made is saved automatically.
Committed State
A state in a database transaction where all changes have been saved and the transaction is complete.
Non-Committed State
A state in a database transaction where changes have not been saved and can be undone.
DDL Tab
A section in database interfaces for data definition language operations.
Comments (in SQL)
Annotations or explanations within the SQL code, ignored during execution.
Beautify Option
A feature in SQL tools to format code for better readability.
Relational Database vs. Non-Relational Database
Logical Connection (for Database Relationships)
The association established between tables in a database through the use of primary and foreign keys,
facilitating data integrity and consistency.