Data science has become an integral part of success in nearly every industry. It is a multidisciplinary field combining STEM disciplines with business insights. As such, it requires not only technical skills, but domain expertise too.
Whether they work in marketing, healthcare, or finance, data scientists need a firm grasp of the basic concepts and trends in the respective field.
In this article, we focus on the history and recent developments in the telecom industry. Then, we explore the types of data and the role of data scientists in telecommunications. Next, we give examples of some common use cases of data science and analytics. Finally, we cover the skills needed to become a data scientist in this sector and provide some useful resources to help you get started.
How to Become a Data Scientist in Telecom: Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Telecom Industry
- Types of Data in the Telecom Industry
- What Is the Role of a Data Scientist in Telecom?
- Use Cases of Data Science in Telecom
- How to Become a Data Scientist in Telecom
- Useful Resources
- How to Become a Data Scientist in Telecom: Next Steps
Introduction to the Telecom Industry
Telecom, short for telecommunication, means communicating over a distance. That could be as near as 1 meter or as far as thousands of miles. As the name implies, the industry is concerned with creating and distributing technology that enables people to communicate over a distance.
Nowadays, the telecommunications sector relies heavily on data and technology. But how did it all start?
To answer this question, we go back in history to the time when people used letters to communicate. Postal offices were the only communication service provider, delivering letters, documents, and presents at great distances.
We can trace back the origins of telecom to the time before the invention of electricity when people used fire signals, pigeons, and messengers by foot and on horseback.
Fast forward to the 1980s and the invention of the World Wide Web. Internet service providers entered the telecom market and changed it forever.
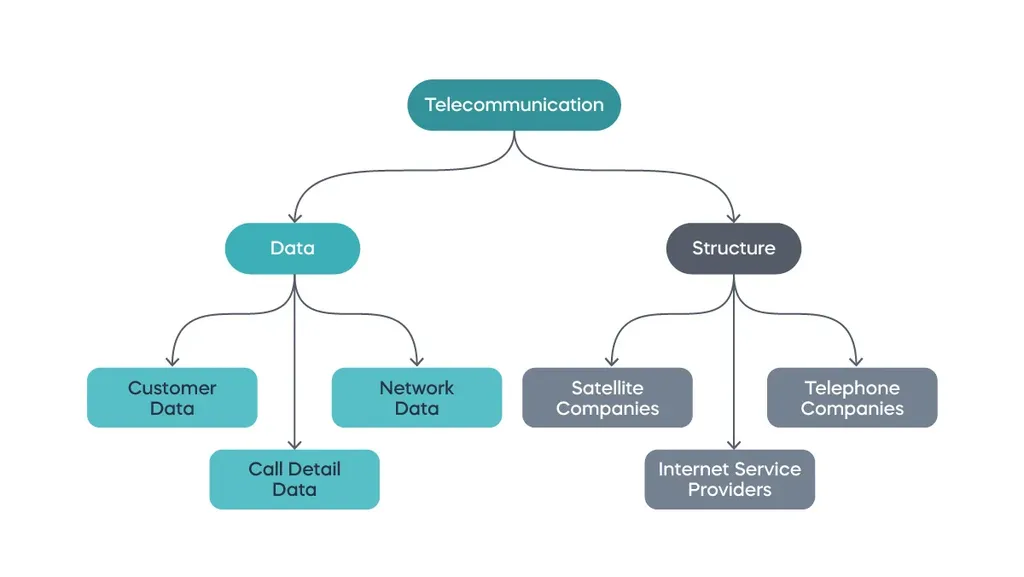
Broadly speaking, today, the telecom industry encompasses the following branches:
- Telephone companies, providing landlines and cellphones
- Cable service companies, offering cable TV and internet
- Satellite companies, delivering internet services through satellite signals or fiber optics
- Internet service providers, selling a wider range of solutions, including web hosting and email services
Types of Data in the Telecom Industry
The telecom sector generates massive amounts of data every minute. Where does it come from?
Data scientists in telecommunication work with customer demographics, payment history, call details, etc. These could be in text, audio, or video format.
To simplify things, let’s put these types of data into categories. Note that this categorization is not exhaustive and uniform. It could vary depending on the region, regulations, and so on.
Still, it gives a good idea of the information you as a data scientist may encounter in your daily tasks.
Customer Data
Telecom companies have millions of users. To deliver their services, they need information like name, address, bank and subscription plan details, and more.
This data is often gathered when the client signs up for the service, and it must be kept confidential.
Call Detail Data
This type of data is typical for the telecommunications sector. With millions of calls made every day, imagine the amount of information generated.
Companies record and save details like the call duration, location of the caller and receiver, the average number of calls per day, etc.
Network Data
Telecom service providers manage, store, and analyze network data to support different functions. Unlike the previous examples, this is not information about the customers, but about the equipment and its configurations.
A database of this type may include the date and time of using the network, certain events (e.g., a network component generating a message), the name of the component, etc.
What Is the Role of a Data Scientist in Telecom?
Although the concrete responsibilities may vary by company, a data science job in telecom would involve the following tasks:
- Work with real-time data to satisfy the ever-changing user requirements. Real-time analytics combine insights from different sources to create the best experience for customers.
- Build machine learning models to detect network failures.
- Reduce customer churn using predictive analytics to detect changes in usage habits and Natural Language Processing to extract user feedback from social media platforms.
- Improve customer experience by analyzing historical data to understand user preferences and optimizing the services accordingly.
- Collaborate with other data scientists to build machine learning algorithms for fraud detection.
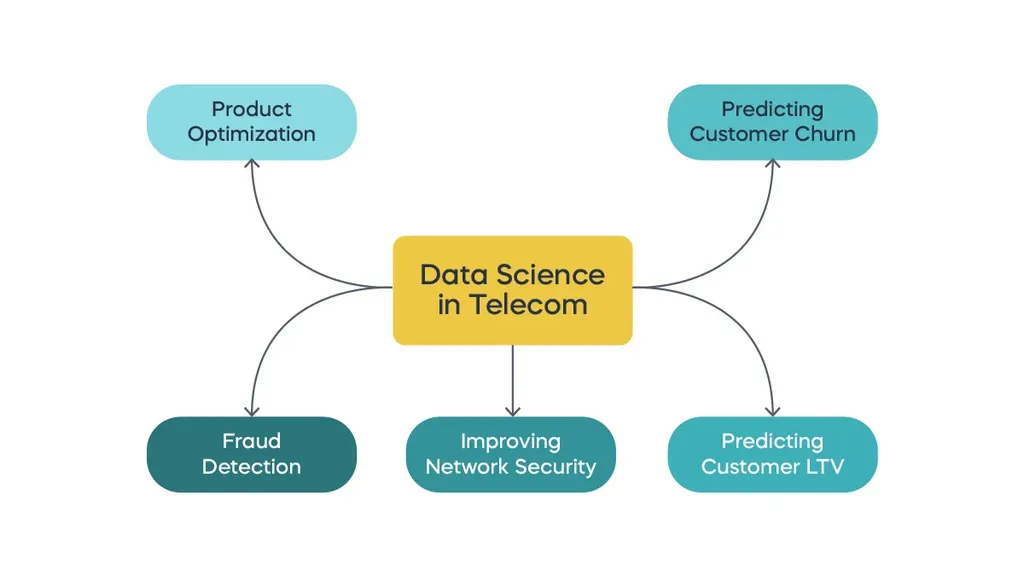
Use Cases of Data Science in Telecom
Data science and big data have multiple applications in telecommunications. These are the most common ones:
- Building customer churn prediction models to help retain clients.
- Using data analysis to optimize telecom products and services.
- Predicting customer lifetime value and providing insights to increase it.
- Develop fraud detection tools using unsupervised machine learning to recognize unusual behavior.
- Improving network security with the help of predictive models to detect and prevent issues.
How to Become a Data Scientist in Telecom
Data science jobs in telecommunications require domain knowledge and technical skills. Let’s go through these requirements step by step.
Domain Knowledge
The resources section below is a good starting point for obtaining the industry-specific theoretical knowledge and technical skills to succeed in telecom.
Most importantly, you need a good understanding of communication networks and how they’re managed, supported, and implemented.
If you don’t have a background in telecom engineering, consider taking a course to get familiar with the basics.
Make sure to apply everything you learn. If you don’t have relevant work experience, demonstrate you can implement your knowledge by creating a data science portfolio with industry-specific projects.
Big Data
The advancement of technology has made communication easier, faster, and more efficient. As a result, the industry generates and uses huge amounts of data.
To become a data scientist in this sector, you need to be familiar with the applications of big data for telecom. This includes implementing best practices for cleaning, analyzing, and of course, storing the information.
Experience with cloud software, such as AWS, will be considered a huge advantage. But more on that later.
Programming Language
As for any other data science position, you need to learn Python and SQL. The latter is particularly important, as managing big databases will be a crucial part of your job.
In addition to basic programming, you need to acquire some big data analytics skills specific to telecommunications.
For example, you must have a good command of Chef. This is a configuration management application, which uses Ruby as its reference language. It’s called Chef because the programs resemble cooking recipes in structure.
Machine Learning
Machine learning has multiple applications in telecom.
For example, companies could draw useful insights from historical data with the help of predictive algorithms. This will help improve their services and meet customers’ expectations.
In addition, data scientists could apply unsupervised machine learning algorithms to detect unauthorized access or unusual activity on someone’s account.
These are key examples of the use of big data in telecommunications.
Machine learning is one of the main areas of expertise that differentiate data scientists from data analysts.
Hands-on Experience
The perfect telecom data analyst resume would contain experience with cloud solutions and platforms like AWS and Azure, as well as communications networks, such as LAN, WAN, WLAN, and MAN.
If you need help building your resume, use the 365 Course on Starting a Career in Data Science as a guideline. In it, industry expert Ken Jee walks you through the project portfolio, resume, and interview preparation process.
Useful Resources
You don’t have to be an engineer to work in the telecom industry.
With the skills mentioned in this article, you can compete with other candidates and secure a role as a data scientist in telecom.
To help you get started, we put together a list of useful courses and readings.
Courses
In this course, you will learn about Python’s technical advantages, specific features, modules, functionalities, and more.
SQL is a must if you are working with databases. This course will teach you everything about database management and creating SQL queries.
This course begins with the very basics of statistics and builds up your arithmetic thinking. It teaches you how to conduct complex analyses and work with different statistical approaches.
You will learn how to gain insights from customer data and use machine and deep learning to perform customer analytics. This is a highly valuable and rare skill set to have as a data science or analytics expert in telecom.
The focus here is on predictive modeling via an array of approaches, such as linear and logistic regression, cluster analysis, etc. The course combines comprehensive theory with practice to exercise your Python skills.
Readings
- Data Scientist Career Path: How to Become a Data Scientist
- The Best Industries for Data Science Specialists
- How to Choose the Right Data Science Course for You in 3 Easy Steps?
- Traditional Data and Big Data Processing Techniques
- Data Science Roles in Telecom Industry
- How Your Telecommunications Experience Will Help You Launch a Career in Data Science
- Telecommunications Industry
- What Is the Telecommunications Sector?
- Data in Telecom: Key Asset and Key Risk
How to Become a Data Scientist in Telecom: Next Steps
The use cases of data science in telecom are numerous. To obtain a job in the sector, you need an array of technical skills and domain knowledge.
You can start with the 365 Data Scientist Career Track. It begins from the very basics and builds up all the way to advanced specialization with a myriad of practical exercises and real-world business cases. If you want to see how the training works, try a selection of free lessons by signing up below.





