Data science is a multidisciplinary field. Not only does it require good coding skills and an analytical mindset, but also domain expertise, which is one of the obvious differences between data analysis and data science. And since data science has become an integral part to drive success in nearly every industry, these professionals should have expertise in the domain they’re working in – for example, the trends of data in agriculture.
In this article, we’ll explore the green world of agriculture and understand its importance for local and global communities. We’ll learn the different data types involved, as well as the needed skills for you to become a data scientist in this field – including what kind of tasks you might do regularly. We’ll also look at the real-life applications of big data in agriculture. Finally, we’ll go through some exciting resources that will serve you as a simple roadmap to get going.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Agriculture
- What Are the Types of Data in Agriculture?
- What Are the Applications of Data Science in Agriculture?
- What Is the Role of a Data Scientist in Agriculture?
- What Are the Required Skills to Become a Data Scientist in Agriculture?
- Useful Resources
- How to Become a Data Scientist in Agriculture: Next Steps
Introduction to Agriculture
While countries like Qatar and Andorra rely mostly on industry to drive growth, agriculture represents the lifeblood of many nations such as Liberia and Somalia. For them, agriculture accounts for as high as 70% of the country’s GDP. Based on this, we can safely say that it is as critical for communities as healthcare. But what is the first thing that comes to mind when you think of agriculture? For most people, it’s the harvest of fruits or vegetables, isn’t it? But this is actually a common misconception – that kind of produce is just a small sliver of what the practice deals with.
Agriculture is both an art and a science. It’s considered one of the oldest professions in the world.
In ancient times, the only tools provided to grow crops were water (to irrigate lands) and fire (to control the growth of some plants). However, over time, farmers developed new tools and techniques to increase productivity. Now we can see entire farms where data science plays an astounding role in managing the process.
What Are the Types of Data Used in Agriculture?
There are different processes involved in agriculture. Each stage generates huge amounts of data. In fact, agriculturists have been collecting data for a long time without even knowing it. For example, a farmer is often aware of the suitable conditions for each plant and assesses factors like:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Time of harvesting
All of these, and more, make up the critical information necessary to grow crops the right way with the least losses possible.
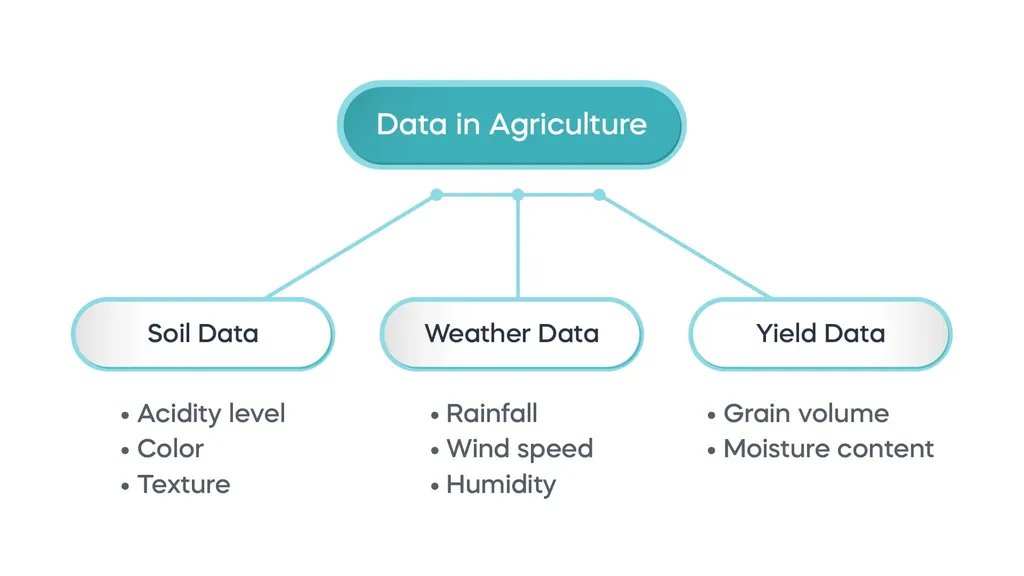
We can categorize agricultural data in different ways according to the purpose of classification. Here, we’ll show the most important data types that you’ll likely deal with in your work, which are also the same ones farmers now need to manage their farms and crops.
Soil Data
This type of data is collected both manually and with equipment that farmers use to analyze small samples of soil to determine its properties. There are many soil parameters, most of which are analyzed chemically.
Although data analysis methods vary from country to country and from one agricultural region to another, here is a list of the most common parameters:
- Acidity (PH level)
- Color
- Texture
- Phosphorous content
- Potassium content
- Organic matter
Yield Data
Yield mapping data is collected using equipment that collects geo-referenced information which agriculturists can use to check the harvested crops and define the problematic areas through digital maps. In simpler terms, this type of data in agriculture helps farmers assess their land visually, as well as monitor performance and productivity.
Weather Data
With the technological advancement of the 21st century, weather data is now collected by sensors in weather stations. What does this mean for agriculture? As previously mentioned, farmers need to be always aware of weather conditions throughout the year as this helps them asses how their harvest will grow. For example, using this type of information, they can decide the right temperature for each crop and the right time to apply pesticides since weather data can help predict pests and diseases on crops.
What Are the Applications of Data Science in Agriculture?
Farmers benefit from data-driven agriculture when making decisions for their land. More specifically, with the huge amounts of data generated every day, they depend on AI systems to provide them with actionable insights in order to increase yield and detect problems beforehand.
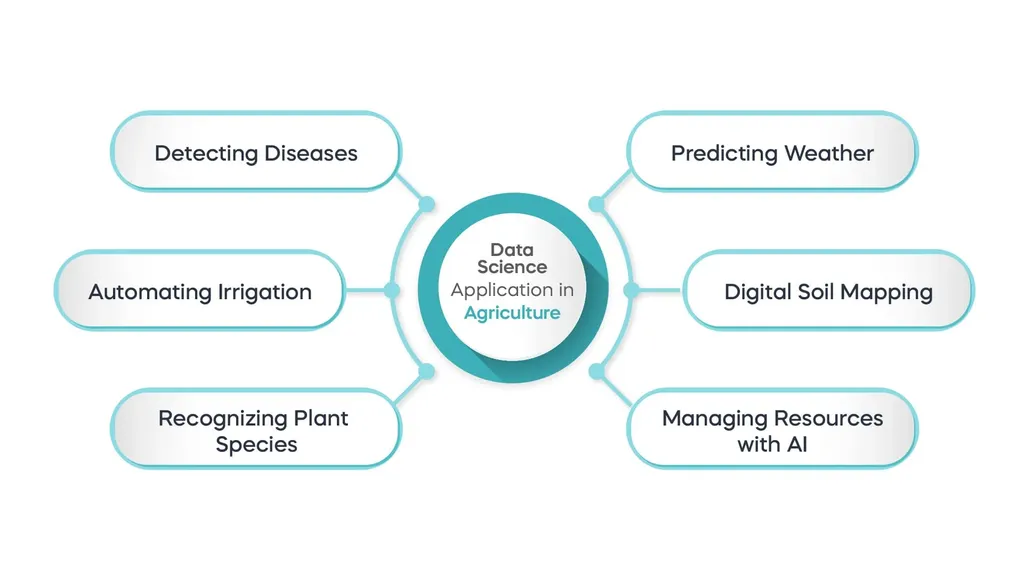
Each company uses data science according to the available human and material resources. It’s important to remember that you need various equipment to collect the required data. To keep it short, these are the most common applications of data science in agriculture:
- Predicting weather conditions such as rainfall, wind speed, and relative humidity.
- Detecting diseases using algorithms that can identify specific patterns in crop images.
- Automating the process of irrigation with the help of weather prediction to help rationalize water consumption.
- Recognizing different plant species using deep learning techniques such as CNN on leaf vein patterns.
- Managing resources like energy, water, and pesticides using AI insights.
What is The Role of a Data Scientist in Agriculture?
If you look up the job description for a “data scientist in agriculture”, you’ll find different results each time because the nature of responsibilities differs according to the country, the company’s scope, the business model, etc. Since we can’t summarize all the key responsibilities – as there are too many – we’ll present the most common ones:
- Collect, analyze and store different data types from different sources to support decision-making.
- Help in developing data pipelines for automation and scalability.
- Work with other data scientists on building machine learning models to predict weather conditions and plant diseases.
- Understand customers’ requirements and apply problem-solving techniques.
- Write scientific reports with sophisticated visualizations to communicate findings to stakeholders.
What Are the Required Skills to Become a Data Scientist in Agriculture?
There’re various career opportunities for aspiring data scientists in the field of agriculture – you can be an agricultural data scientist, an environmental analytics scientist, an agriculture sustainability analyst, and many more.
In the previous section, we mentioned that each position requires a certain set of skills depending on the country and the company. However, there are some common basics you need to be aware of if you wish to apply for data science jobs in agriculture:
Domain Knowledge
Domain knowledge is a prerequisite to working as a data scientist in any field. In this specific case, you need to be familiar with the science of agriculture, its techniques, terminology, and advancements. You may study an introduction to farming, the effect of water and different weather conditions on plants, and how analytics and machine learning are used to improve agriculture in practice.
Some positions may require that you hold a postgraduate degree in the specific domain you’re applying for, there’re many opportunities for you to qualify as a candidate if you take the right steps and show you have a passion for learning.
If you are new to the field and currently looking for your first professional role, read 365’s article on how to become a data scientist with no experience.
Programming
Fluency in at least one programming language is a must for any data-related role. The easiest one to use is Python but sometimes you may need to use R if you’re running advanced statistical analysis. If you’re just starting, however, focus on specializing in one language first. Learn the basics of Python to analyze different types of data, as well as to train and build machine learning models later on in your journey.
Statistics
It’s nice to be familiar with basic statistical concepts such as measures of spread and correlation. Worried you don’t have the proper qualifications? Don’t worry, you don’t have to be a Math graduate to solve data problems in agriculture. Just focus on the key concepts:
Descriptive Statistics
As the name implies, this branch of statistics is used to describe the main characteristics of data. It includes the calculation of mean, mode, and median.
Inferential Statistics
This is another branch of statistics that analyzes random samples to draw conclusions about a population. This branch is divided into hypothesis testing and regression analysis.
Variability
Variability includes parameters like range, standard deviation, and variance.
Correlation
Correlation is a simple method for measuring the relationship between two variables. We recognize these two types:
- Positive correlation: one variable increases with the increase of the other, i.e. they move in the same direction.
- Negative correlation: one variable increases with the decrease of the other or vice versa, i.e. they move in the opposite direction.
Machine Learning
The final application for data in agriculture we’ll look at is machine learning. From detecting diseases in plants to predicting the weather, knowing how to use different algorithms is a big advantage. Moreover, it is quite useful in almost every aspect of agriculture, so you need to learn the classification of ML algorithms and when to use each one.
As mentioned, the responsibilities are wideset and depend entirely on the role you’re taking on in a specific company. However, in order to better prepare for your career as a data scientist in agriculture, we suggest you brush up your skills in the aforementioned areas. A good way to do so is by taking the 365 Data Scientist Career Track which streamlines your progress in a structured way.
Useful Resources
If things seem overwhelming at the beginning, it’s totally fine! As the famous proverb goes, “the journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step”. Of course, a thousand miles is an exaggeration here, but even if you have just as many to take in order to reach your goal, now is the time to put your foot forward with the following resources.
Data Science Courses
Here, we’ll share some useful online courses, led by the experts at 365 Data Science, that will build your data skills.
This course will introduce you to the world of Python. You will learn about Python’s technical advantages, specific features, modules, functionalities, and more.
SQL is a must if you are expected to work with databases. This course is the ultimate guide, teaching you everything you need to know in terms of database management and creating SQL queries.
This course begins with the very basics of statistics and builds up your arithmetic thinking. It gradually teaches you how to work with more complex analyses, statistical approaches, and hypotheses.
This course is focused on predictive modeling via an array of approaches such as linear regression, logistic regression, and cluster analysis. It combines comprehensive theory with lots of practice to allow you to exercise your Python skills.
This course will teach you the inner workings of deep neural networks with an emphasis on the why and how of things. You will see the theory implemented in practice with the powerful framework TensorFlow 2.0.
Further Reading
To further help you on your journey, here is a selection of resources you can use to enrich your domain knowledge and, thus, increase your chances of landing that data science role in the field of agriculture:
- The Art and Science of Agriculture
- Introduction to Agriculture and Agronomy
- Using Data to Drive Decisions
- Data Science In Agriculture
- Data Science in Agriculture – Advancing Together & Benefiting Farmers
- 5 Ways Data Science is Transforming Agriculture
- How Is Machine Learning Used in Agriculture?
- How To Use Data Science In Agriculture To Predict Yield And Diseases
How to Become a Data Scientist in Agriculture: Next Steps
If applying data science to the field of agriculture sounds like the right career path for you, take the time to study the domain and build your data skills. The learning journey is indeed long, but it doesn’t have to be overwhelming.
The 365 Data Science Program offers high-quality online education on a wide variety of topics that cover the all-encompassing field of data. Starting from the very basics, the courses and supplementary materials will help you specialize in your chosen role, whether that is a data scientist, machine learning engineer, or business analyst. Sign up for free below to get a taste of the teaching style and more.





